Genes
Every child inherits genes from both of their biological parents and these genes in turn express specific traits. Some of these traits may be physical for example hair and eye color and skin color etc. Some genes may also carry the risk of certain diseases and disorders that may pass on from parents.
The genes lie within the chromosomes, chromosomes come in pairs. Each cell in the human body has 23 pairs of these small thread-like structures in the nucleus of their cells. 23 or half of the total 46 comes from the mother while the other 23 comes from the father.
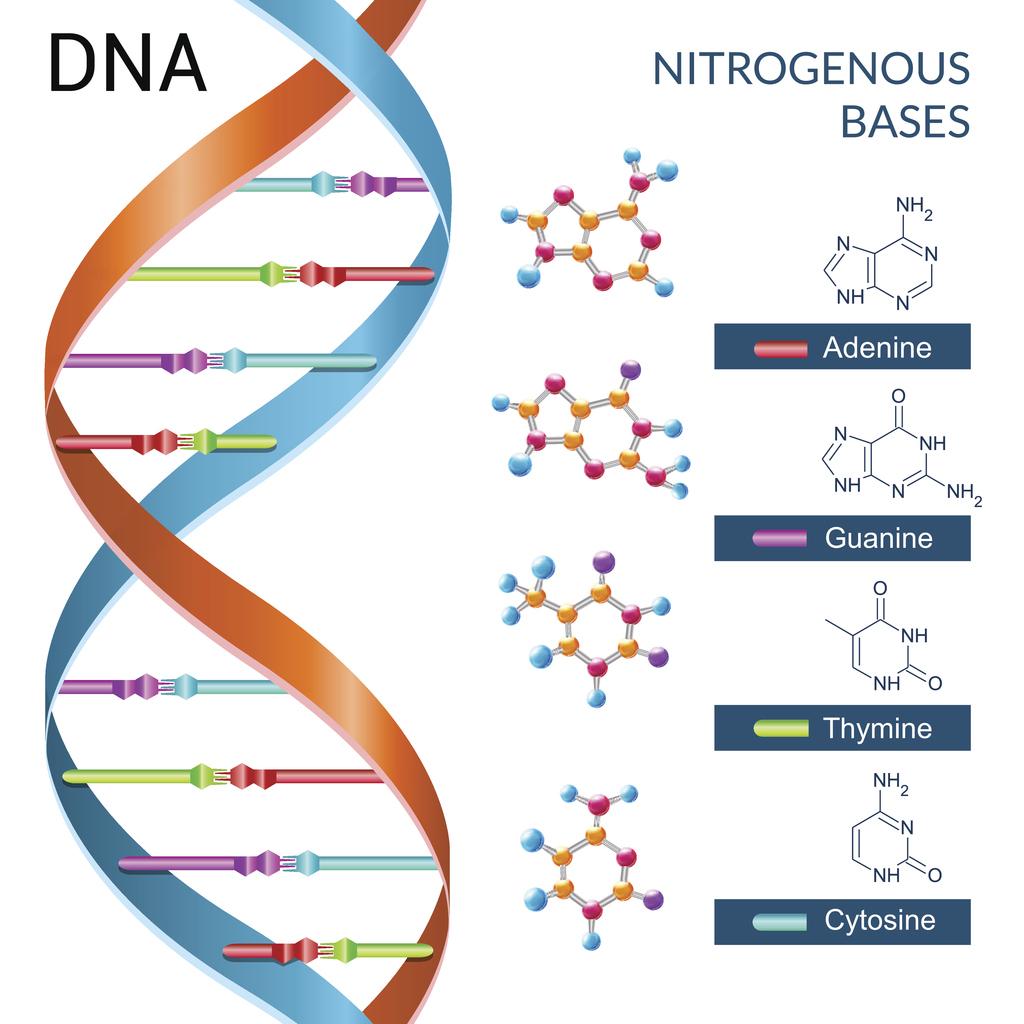
The chromosomes, and therefore the genes, are made up of the chemical substance called DNA. The information in DNA is stored as a code made up of four chemical bases: adenine (A), guanine (G), cytosine (C), and thymine (T). DNA is the material that holds genes. It is the building block of the human body.
The chromosomes are very long thin strands of DNA, coiled up tightly. Each chromosome has a constriction, called the centromere. The centromere divides the chromosomes into two ‘arms’: a long arm and a short arm. Chromosomes are numbered from 1 to 22 and these are common for both sexes and called autosomes. There are also two chromosomes that have been given the letters X and Y and termed sex chromosomes. The X chromosome is much larger than the Y chromosome.
Epigenetic
Epigenetics is a system of turning genes off and on.
It refers to external modifications to DNA that turn genes “on” or “off.” These modifications do not change the DNA sequence, but instead, they affect how cells “read” genes.
Factors affect Epogenetic and health:
1- Lifestyle
2- Enviromental
3- Dite
4- Medicines
5- Feelings
6- Age
Epigenetic marks they are still modifiable by lifestyle choices and environmental influence. There are numerous examples of epigenetics that show how different lifestyle choices and environmental exposures can alter marks on top of DNA and play a role in determining health outcomes.
The environment is a powerful influence on epigenetic tags and disease susceptibility. Pollution has become a significant focus in this research area as scientists are finding that air pollution could alter methyl tags on DNA and increase one’s risk for neurodegenerative disease.
Diet has also been shown to modify epigenetic tags in significant ways. The field of nutriepigenomics explores how food and epigenetics work together to influence health and wellbeing. For example, a study found that a high fat, low carb diet could open up chromatin and improve mental ability via HDAC inhibitors. Other studies have found that certain compounds within the foods we consume could protect again cancer by adjusting methyl marks on oncogenes or tumor suppressor genes. An epigenetic diet may guide people toward the optimal food regimen as scientific studies reveal the underlying mechanisms and impact that different foods have on the epigenome and health.
There is growing evidence that alcohol and drug use can cause lasting genetic changes that may reinforce substance addiction that could also be passed down to future generations. The researches provide compelling evidence for a link between drug-induced epigenetic regulation of gene expression and drug abuse-related behavior in animals. The epigenetic changes in gene expression occur in brain regions involved in reward learning and motivation. This leads to plasticity-related changes within the neurocircuitries that mediate these processes and is associated with aberrant behaviors that resemble hallmark symptoms of human drug addiction.
When we have negative emotions such as anger, anxiety and dislike or hate, we experience stress and our energy reserves are redirected,
This causes a portion of our energy reserves, which otherwise would be put to work maintaining, repairing and regenerating our complex biological systems, to instead confront the stresses these negative thoughts and feelings create.
But when we activate the power of our hearts’ with positive emotions
means instead of the drain and damage stress causes to our bodies’ systems, we are renewed mentally, physically and emotionally. The more we do this the better we’re able to ward off stress and energy drains in the future. Heartfelt positive feelings fortify our energy systems and nourish the body at the cellular level.
In simple terms most people can relate to, what this means is that when we are having a bad day, going through a rough period such as dealing with the sickness of a loved one or coping with financial troubles, we can actually influence our bodies – all the way down to the cellular level – by intentionally thinking positive thoughts and focusing on positive emotions.
Aging is an inevitable outcome of life, characterized by progressive decline in tissue and organ function and increased risk of mortality.